
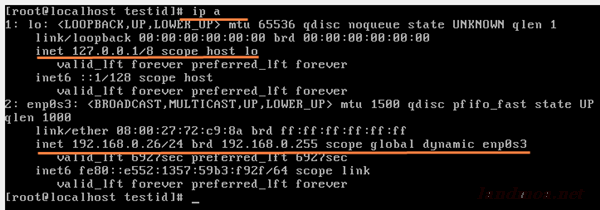
Centos 7 static ip not working manual#
However, this is not recommended because the manual configuration of IPv6 is prone to errors and is quite arduous.įurthermore, it’s quite a task keeping track of which IPv6 addresses are assigned to what systems. Just like IPv4, a manual configuration of IPv6 is possible using the nmtui and nmcli tools. To apply the changes, reboot your system. In the line, GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX, append the argument ipv6.disable=1 at the end of the line as shown. To permanently disable IPv6, edit the GRUB /etc/default/grub file. Let us configure our system for the following information. Configure Static IP Address in CentOS 7 / RHEL 7. But, if you go to the bigger organizations, they use static (manual) IP to avoid network issues due non-availability of DHCP servers.
Centos 7 static ip not working how to#
Then restart NetworkManager for the changes to apply. READ: How To configure DHCP server on CentOS 7, Ubuntu 18.04 & Debian 9. To enable IPv6, run the command: $ sudo sysctl -w .disable_ipv6=0 (Everything is working fine when i set ip to DHCP ) I put my configurations as below. but Virtual machines and hosts can't ping each other and can't connect to network.

I need to config my linux server ip to static. To temporarily disable IPv6, run the command: $ sudo sysctl -w .disable_ipv6=1 This issue was bothering me for many days. $ ip aīe on the lookout for the inet6 prefix as shown below. But, if you’re using a wired workstation or you don’t have a lot of configuration dependent on the VM’s IP address, bridged networking might be a good solution to get you both internet access and host. On the terminal, you can check the IPv6 address of your interfaces by running the IP commands below. Also, I really need a static IP address for the VM to configure the Ansible scripts and because part of the process is to generate a self-signed SSL certificate for the VM’s IP address. The output above confirms that IPv6 addressing is enabled.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
